How Excel Links Not Working can Save You Time, Stress, and Money.
Facts About Excel Links Not Working Uncovered
Table of ContentsThe Best Guide To Excel Links Not WorkingThe 7-Minute Rule for Excel Links Not WorkingExcel Links Not Working Can Be Fun For EveryoneAll About Excel Links Not Working8 Simple Techniques For Excel Links Not Working
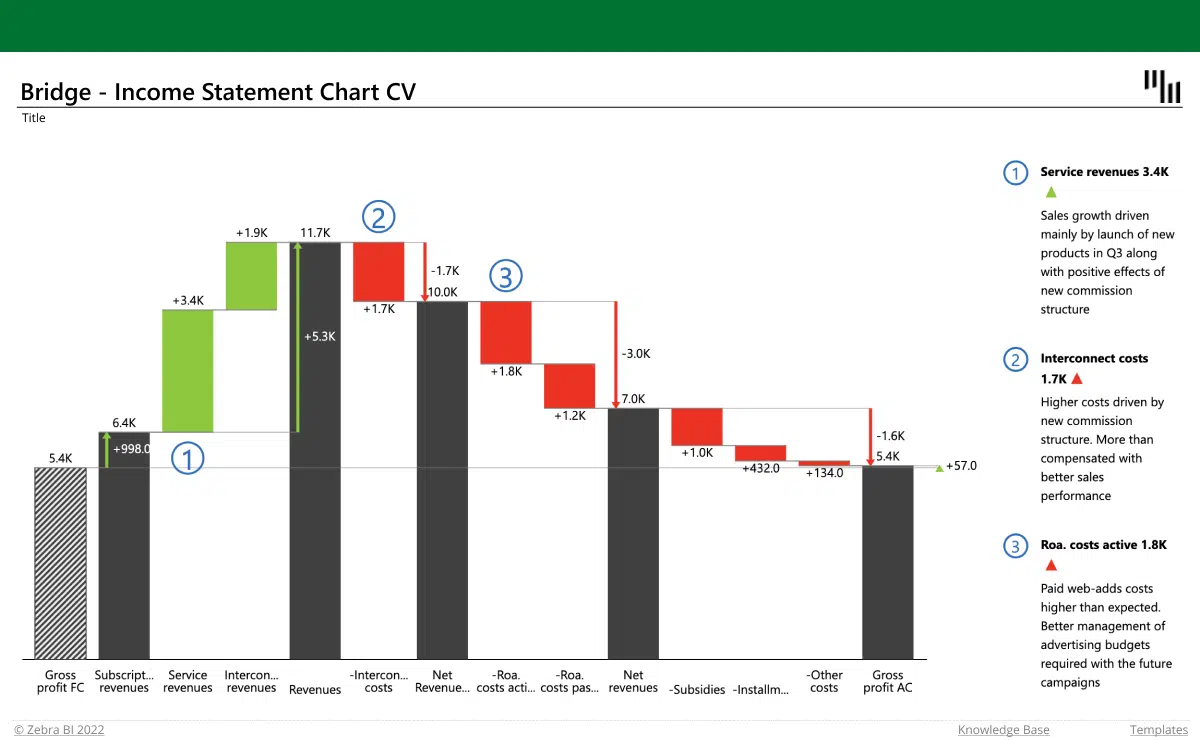
Nonetheless, array calculation features like either can not take care of whole column referrals or determine all the cells in the column. User-defined features don't instantly identify the last-used row in the column as well as, consequently, regularly compute entire column recommendations inefficiently. Nonetheless, it is easy to program user-defined features to ensure that they acknowledge the last-used row (excel links not working).
Some Known Incorrect Statements About Excel Links Not Working
Using the formula for a vibrant range is typically more effective to the formula since has the disadvantage of being an unstable feature that will be computed at every recalculation. Efficiency reduces due to the fact that the function inside the dynamic array formula have to check out many rows. You can reduce this efficiency decline by keeping the part of the formula in a different cell or defined name, and after that describing the cell or name in the dynamic range: Counts!z1=COUNTA(Sheet1!$A:$A) Offset, Dynamic, Variety=OFFSET(Sheet1!$A$ 1,0,0, Counts!$Z$ 1,1) Index, Dynamic, Variety=Sheet1!$A$ 1: INDEX(Sheet1!$A:$A, Counts!$Z$ 1+ROW(Sheet1!$A$ 1) - 1,1) You can also make use of features such as to construct vibrant ranges, however is unpredictable and also always determines single-threaded.
Making use of multiple vibrant varieties within a solitary column needs special-purpose counting features. Making use of numerous vibrant arrays can lower performance. In Workplace 365 version 1809 and also later on, Excel's VLOOKUP, HLOOKUP, as well as MATCH for specific match on unsorted data is much faster than ever before when searching for numerous columns (or rows with HLOOKUP) from the very same table range.
There are numerous means of boosting lookup estimation time. If you use the precise match choice, the estimation time for the feature is proportional to the number of cells scanned before a match is discovered. For lookups over large varieties, this time can be substantial. Lookup time utilizing the approximate suit options of,, and on arranged data is rapid and is not dramatically raised by the size of the range you are searching for.
The Buzz on Excel Links Not Working
Make sure that you comprehend the match-type and also range-lookup options in,, and also. The complying with code instance reveals the syntax for the feature. SUIT(lookup value, lookup range, matchtype) returns the biggest match less than or equivalent to the lookup value when the lookup array is sorted rising (approximate suit).
The default option is approximate match sorted rising. The following code example reveals the phrase structure for the and also functions.
VLOOKUP(lookup value, table selection, col index num, range-lookup) HLOOKUP(lookup worth, table variety, row index num, range-lookup) returns the biggest suit less than or equal to the lookup value (approximate suit). Table array look at this now must be sorted ascending.
Unknown Facts About Excel Links Not Working
If your data is sorted, however you desire a precise match, see Usage two lookups for arranged data with missing worths. Try using the and operates rather than. Is a little much faster (about 5 percent much faster), easier, and utilizes less memory than a combination of as well as, or, the extra versatility that as well as offer frequently allows you to substantially conserve time.
The feature is fast and is a non-volatile function, which speeds up recalculation. The function is also fast; nonetheless, it is an unstable function, as well as it often considerably raises the time taken to process the computation chain. It's easy to transform to as well as. The following 2 declarations return the exact same answer: VLOOKUP(A1, Information!$A$ 2:$F$ 1000,3, False) INDEX(Data!$A$ 2:$F$ 1000, SUIT(A1,$A$ 1:$A$ 1000,0),3) Because specific match lookups can be sluggish, take into consideration the complying with options for enhancing performance: Utilize one worksheet.
When you can, the information first (is fast), and also discover this utilize approximate suit. When you need to utilize an exact match lookup, limit the variety of cells to be scanned to a minimum. Usage tables and structured references or vibrant variety names rather than referring to a multitude of rows or columns.
The Greatest Guide To Excel Links Not Working
2 approximate matches are considerably faster than one specific match for a lookup over greater than a couple of rows. (The breakeven point is regarding 10-20 rows.) If you can arrange your data however still can not use approximate match since you can not make certain that the worth you are looking up exists in the lookup range, you can utilize this formula: IF(VLOOKUP(lookup_val, lookup_array,1, True)=lookup_val, _ VLOOKUP(lookup_val, lookup_array, column, Real), "notexist") The first component of the formula works by doing an approximate lookup on the lookup column itself.
VLOOKUP(lookup_val, lookup_array, column, True) If the answer from the lookup column did not match the lookup value, you have an absent value, as well as the formula returns "notexist". Be aware that if you seek out a worth smaller than the tiniest worth in the list, you receive an error. You can manage this error by utilizing, or by adding a tiny examination worth to the checklist.
Beginning with Excel 2007, you can make use of the feature, which is both simple and quick. IF IFERROR(VLOOKUP(lookupval, table, 2 FALSE),0) In Recommended Reading earlier versions, a simple yet sluggish way is to use a feature which contains two lookups. IF(ISNA(VLOOKUP(lookupval, table,2, FALSE)),0, _ VLOOKUP(lookupval, table,2, FALSE)) You can avoid the double exact lookup if you utilize exact when, store the result in a cell, and afterwards examine the outcome prior to doing an.